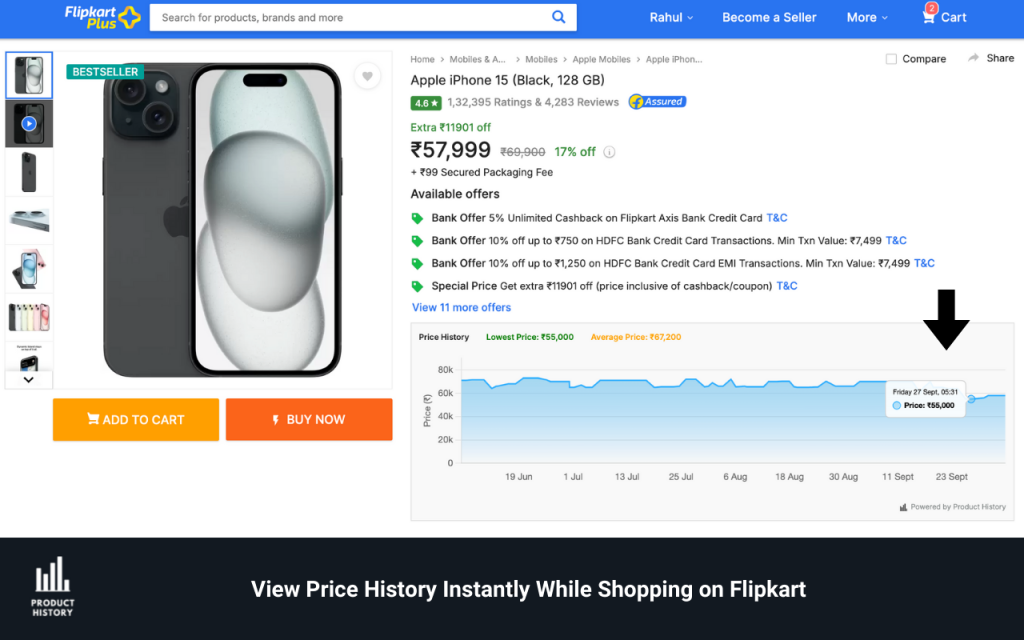
If you’re building a price comparison tool, this guide explains How to Scrape Flipkart Products for Price Comparison while staying compliant with platform terms and laws. It offers a practical, responsible approach to collecting product data for accurate price tracking, competitive analysis, and data-driven decision making. Throughout, you’ll see how to balance value with governance, and how ScraperScoop can help you implement a solid, compliant data workflow.
Why scraping Flipkart data raises both opportunity and risk
Opportunity: Access to real-time or near-real-time pricing data can power smarter pricing, better product recommendations, and more compelling comparisons for consumers.
Risk: Violating Flipkart’s terms of service, hitting rate limits, or triggering blocks can result in access being restricted, legal concerns, or reputational damage.
Takeaway: Prioritize legality and ethics. Use official channels whenever possible, and design data collection to be transparent, respectful of the site’s policies, and sustainable over time.
Safer, compliant alternatives to direct scraping
Use official APIs or partner programs: Some marketplaces offer affiliate or merchant APIs that provide product data, pricing, and availability in a terms-compliant way.
Leverage data providers and feeds: Third-party services offer licensed product catalogs and price feeds designed for price comparison platforms.
Manual or permission-based access: In cases where data needs are narrow, obtain explicit permission from the retailer or work through a formal data-sharing agreement.
Why this matters: This approach reduces risk, ensures data quality, and supports scalable, long-term price-tracking capabilities.
What data to capture for effective price comparison
To build meaningful price comparisons, focus on a well-defined data schema. Typical fields include:
product_id or canonical_id
title and brand
product_url and image_url
current_price and currency
market_price or MRP (if available)
discount percentage and savings
availability/status
seller or marketplace
rating and reviews_count
category and taxonomy (e.g., electronics > mobiles)
timestamp (UTC)
price_history (temporal list of price entries)
last_scraped_at and source_platform (Flipkart)
notes on any price modifiers (coupon applicability, bank offers) Remember to normalize variations (e.g., color or storage options) so you’re comparing like with like.
High-level approach to a compliant data collection workflow
Define scope and data model: Specify products or categories to monitor, and the exact fields you’ll collect. Align with your business objectives (e.g., banner pricing for Black Friday deals, weekly price trends, or alerting on price drops).
Establish governance and policy checks: Create internal rules for data usage, retention, access, and security. Align with Flipkart’s terms of service and applicable data privacy laws.
Respect site policies and robots.txt: Review Flipkart’s robots.txt and terms to understand allowed crawling practices, rate limits, and any disallowed actions.
Plan crawl frequency and throttling: Use conservative request intervals and randomized delays to minimize load on Flipkart’s servers and reduce the risk of blocks.
Implement robust data validation: Validate data types, normalize price formats, and flag anomalies (e.g., sudden price spikes without a credible source).
Data storage and lineage: Store raw data and processed data separately. Maintain a clear audit trail with timestamps and source identifiers.
Monitoring and incident response: Set up alerts for access blocks, schema changes on the site, or data quality issues. Have a plan to respond quickly if access is restricted.
Documentation and compliance review: Keep records of data sources, approvals, and policy references to support audits and regulatory reviews.
Data quality, normalization, and deduplication considerations
Canonical product matching: Use stable product identifiers (when available) to deduplicate products across categories and sellers. If Flipkart uses internal SKUs, map them consistently.
Normalize price data: Convert currencies to a common baseline when needed, and store both current and historical prices with precise timestamps.
Handle variants intelligently: For products with multiple variants (e.g., different RAM or color), decide whether to treat variants as separate records or as attributes of a single product.
Detect and resolve data anomalies: Implement checks for missing fields, improbable price values, or inconsistent seller information. Create remediation rules or escalation paths.
Using data for price comparison and business insights
Price trend analysis: Track historical prices to identify long-term trends, seasonal effects, and price cycles.
Discount and offer detection: Identify genuine price drops vs. promotional spikes, and annotate with available offers such as bank discounts or coupon codes.
Black Friday and seasonal boosts: Black Friday and festive seasons typically drive price volatility. Tie this data to promotion calendars to surface timely deals.
Competitive intelligence: Benchmark against other marketplaces to assess competitive positioning, ensuring your use respects licensing and rights.
Alerting and automation: Create price-drop alerts or dashboards that notify teams when a product meets predefined thresholds.
Data governance, security, and storage considerations
Access control: Restrict data access to authorized teams and implement role-based permissions.
Data retention: Define how long price history is kept and when archived data should be moved to long-term storage.
Security safeguards: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit; monitor for unusual access patterns.
Compliance documentation: Maintain an ongoing record of policies, approvals, and data-sharing agreements.
Data quality ownership: Assign data stewards responsible for data quality and integrity.
Semantics, SEO signals, and related terms (LSI) for this topic
Related concepts: web scraping ethics, data extraction, price tracking, product catalog enrichment, structured data, ETL pipelines, data normalization.
LSI keywords you can naturally weave in: Flipkart product data, price history, price tracking, e-commerce data, web crawlers, rate limiting, robots.txt, terms of service, data governance, price comparison engine, market intelligence.
Schema and semantics: Consider aligning your data with schema.org/Product and Offers structures where you publish your results, to improve interoperability and discoverability.
How ScraperScoop supports compliant price data collection
ScraperScoop helps teams implement ethical, compliant data collection workflows for price comparison. Our approach emphasizes governance, proper data licensing, and scalable pipelines that respect platform policies while delivering timely, accurate price data. We provide templated data schemas, validation rules, and monitoring dashboards to keep your price-tracking initiative reliable and auditable. If you’re evaluating a solution, consider a guided demonstration to see how ScraperScoop can streamline data collection, normalization, and delivery for Flipkart and similar marketplaces.
Practical considerations for businesses planning price comparison initiatives
Budget and resources: Weigh the cost of compliant data access vs. the risk and overhead of unauthorized scraping. Licensing and API access often deliver higher ROI with lower risk.
Legal and compliance risk: Always prioritize permissions, terms of service, and regional data privacy requirements. Non-compliance can result in service restrictions or legal action.
Operational resilience: Build redundancy by combining multiple data sources (official APIs, licensed feeds, and cautious, permissions-based scraping where allowed) to ensure continuity.
Time-to-value: A compliant data program can deliver faster time-to-value through repeatable processes and scalable pipelines, compared with ad-hoc manual data collection.
Actionable next steps and recommended workflow
Step 1: Define data needs and obtain permissions where possible.
Step 2: Map a data model with clear fields for price, availability, and lineage.
Step 3: Choose compliant data sources (official APIs, licensed feeds) and establish contracts if needed.
Step 4: Design a governance, security, and retention policy.
Step 5: Build a data pipeline with validation and monitoring dashboards.
Step 6: Launch a pilot focused on a small product set and evaluate data quality and ROI.
Step 7: Scale with additional categories, while maintaining compliance and governance.
Clear call to action for readers
If you’re building a robust price comparison solution and want to keep data integrity, legality, and performance top of mind, explore a compliant data strategy with ScraperScoop. Schedule a demo to see how we can help you design, implement, and govern a price-tracking workflow across Flipkart and other major marketplaces. Subscribe for updates on best practices, legal considerations, and data engineering tips for e-commerce intelligence.
Conclusion: Building trustworthy, actionable price data
Understanding How to Scrape Flipkart Products for Price Comparison in a responsible way starts with policy awareness, the right data sources, and a transparent workflow. By combining compliant access methods with rigorous data governance, you can deliver reliable price insights for consumers and businesses alike, while minimizing risk and maximizing long-term value. Embrace a structured, ethical approach, and leverage trusted partners like ScraperScoop to accelerate your journey from data to trusted price intelligence.
Further reading and resources
Flipkart terms of service and robots.txt considerations
Industry best practices for price tracking and data governance
Use cases for price history and Black Friday deal monitoring
Guide to schema.org/Product and Offers for e-commerce data
How to evaluate API-based vs. scraping-based data solutions
Disclaimer
This article provides high-level, compliant guidance for price-tracking initiatives. Always verify current platform policies and legal requirements before collecting data.